Decision modeling
Scenario
A doctor diagnoses acute sinusitis to a patient. This inflammation can be treated with three different antibiotics: Amoxicillin, levofloxacin, and cefuroxime. The antibiotics can be dosed with 250mg or 500mg. However, only patients that are not allergic to penicillin can be treated this way.
Finally, the doctor has to decide whether a patient needs to stay in hospital during treatment. This depends on the type of antibiotics as well as on the dose.
Patients who are younger than 18 years are treated with cefuroxime, those who are older are treated with amoxicillin. If the age is unknown, levofloxacin is administered. The dosage depends on the age, creatinine value, and creatinine clearance of the patient. Patients between 15 and 60 years are treated with 500mg. Exceptions are made if the patient has a creatinine value higher than 2mg/dl. Then, the clearance has to be calculated with the following formula:
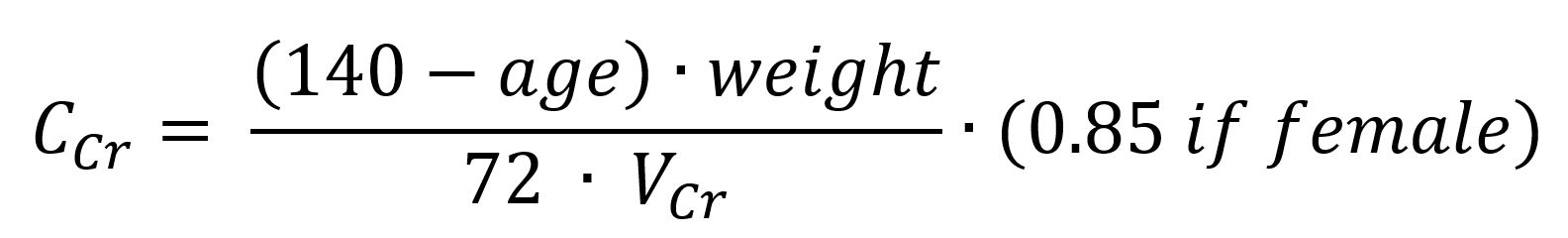
where VCr denotes the creatinine value in mg/dl. If the clearance is below 50, only 250g are administered. If the age is unknown, the dose is 250mg by default.
Only patients who are treated with 500mg or with levofloxacin have to stay in hospital during treatment.
Exercise
For the given scenario, design a DMN decision model that includes the decision requirements and logic. The model should decide whether the patient should be treated stationary, non-stationary, or not be treated but refered to a specialist.